Do you wash your hands thoroughly every time after visiting the bathroom? Be honest with yourself. If the answer is “not always,” a recent study might be enough to make you change your habits.
The study, which was published in Lancet Infectious Disease, highlighted the potential consequences of failing to wash your hands after going to the bathroom. Researchers discovered this habit is more likely to spread E. coli bacteria than eating raw meat. Unfortunately, E. coli is drug-resistant and is potentially fatal.
During the study, researchers in the UK analyzed samples from human sewerage, feces and blood and samples of beef, chicken and pork. They identified similar bacterial strains with the samples taken from humans. But they did find that while the same strains of E. coli bacteria were found in human samples, they are different compared to the ones found in animal meat. This may indicate that although eating meat that is improperly prepared or which is raw can spread E. coli, the primary path of transmission is through humans. Consequently, researchers summarised that poor bathroom hygiene is one of the biggest reasons why these bacteria are spread, most likely through human feces particles.
What Is E. coli?
According to information on HealthLink BC, E. coli (Escherichia coli) is a bacterium found in the digestive tracts of animals and humans.
There are numerous types of E. coli, most of which are harmless, but some strains can cause bloody diarrhea, stomach cramps and nausea and vomiting. Some could also cause kidney failure or severe anemia, potentially leading to death. Other strains of E. coli can cause other infections including urinary tract infections. Usually, it takes about a week to recover from E. coli.
Often, people won’t see a doctor for treatment and don’t realize E. coli caused their symptoms.
You are most likely to get E. coli if you encounter feces of humans or animals and which can happen if you eat or drink food and water contaminated with feces. E. coli can enter meat during processing and if the meat isn’t cooked to 71°C, E. coli bacteria will survive and will infect whoever consumes them. Also, any food that contacts contaminated raw meat will become infected. Other sources of E. coli include raw milk or dairy products which is why these products are often pasteurized, where they are heated to destroy bacteria.
Often, people won’t see a doctor for treatment and don’t realize E. coli caused their symptoms.
A Quick Refresher on Washing Your Hands Thoroughly
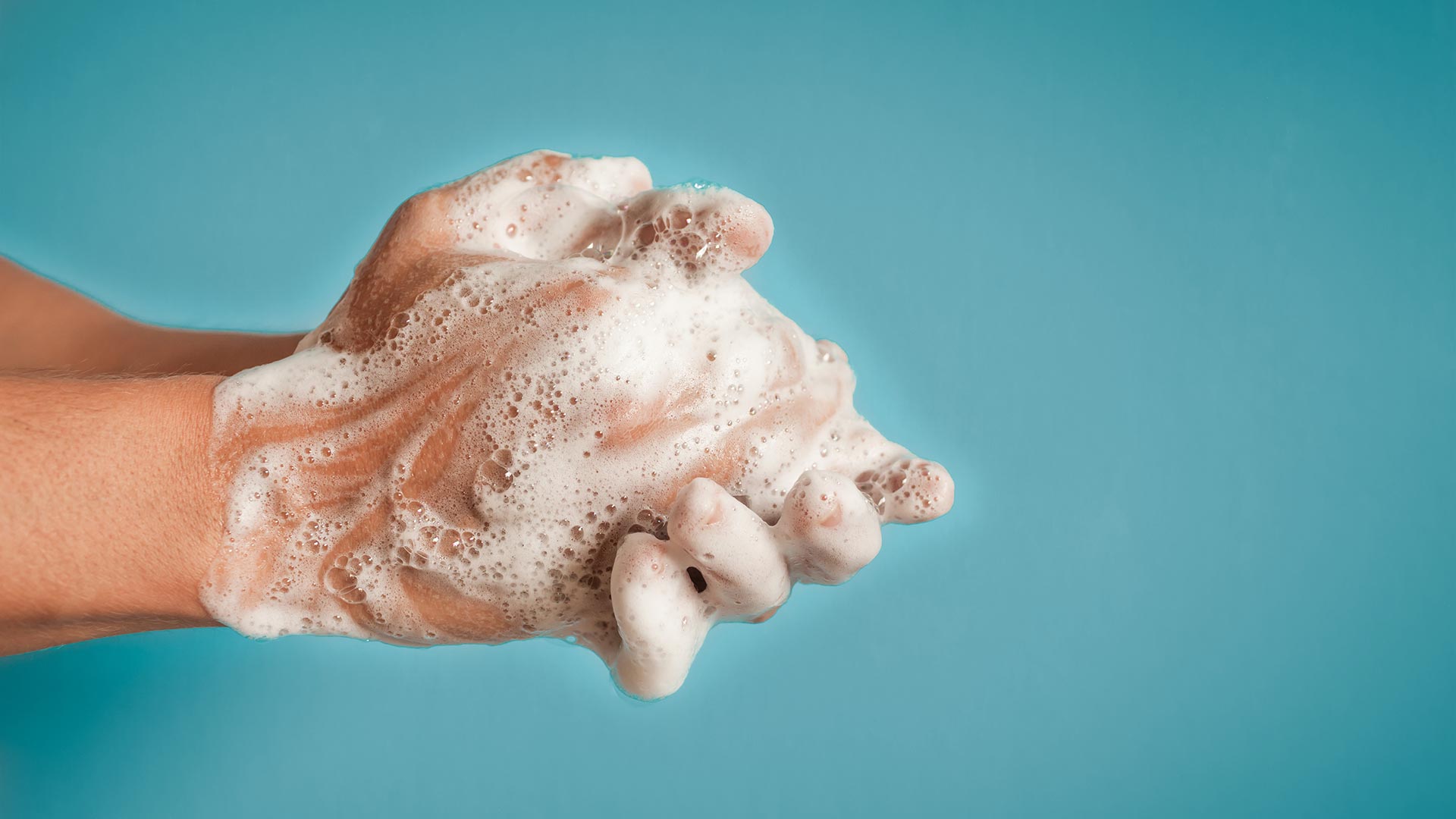
Most of us are guilty of washing our hands too quickly or failing to use enough soap. Merely rinsing your hands with water or giving them a quick once over with soap isn’t enough. Read our quick refresher on how to do it properly:
- Wet your hands under warm running water and use a mild soap to work up a good lather. Wash your hands all the way up to your wrists and scrub them for at least 15 to 20 seconds. For reference, most of us only wash for about six seconds.
- When washing your hands, be sure to cover all surfaces, including below your fingernails, between your fingers and the backs of your hands and wrists.
- Once you have finished washing your hands, rinse them thoroughly under running water.
- If you are using a public bathroom, it’s a good idea to use a paper towel to open the door. Door handles are often covered in bacteria.